Hep C State Policy Simulator
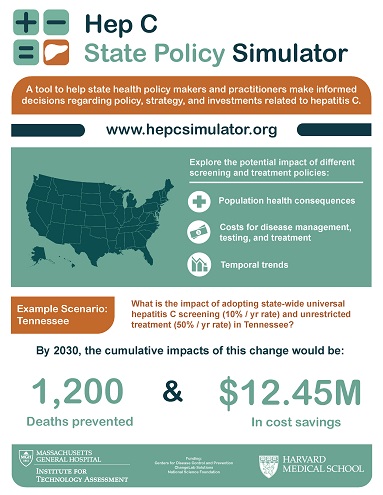
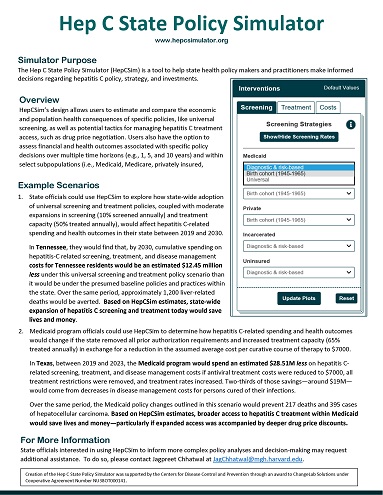
 The Hep C State Policy Simulator (the Simulator) is a tool to help state health policy makers and practitioners make decisions regarding policy, strategy, and investments related to hepatitis C. With the simulator, you can explore the potential impact of different screening and treatment policies and cost drivers. This information is designed to help states evaluate the short- and long-term economic and public health consequences of specific policies (e.g., universal screening), as well as potential tactics (e.g., drug price negotiations) for managing hepatitis C with constrained resources. In addition, you can use the simulator to assess the fiscal and health outcomes associated with specific policy decisions within and across subpopulations (i.e., Medicaid, Medicare, privately insured, uninsured individuals, and state prison inmates).
The Hep C State Policy Simulator (the Simulator) is a tool to help state health policy makers and practitioners make decisions regarding policy, strategy, and investments related to hepatitis C. With the simulator, you can explore the potential impact of different screening and treatment policies and cost drivers. This information is designed to help states evaluate the short- and long-term economic and public health consequences of specific policies (e.g., universal screening), as well as potential tactics (e.g., drug price negotiations) for managing hepatitis C with constrained resources. In addition, you can use the simulator to assess the fiscal and health outcomes associated with specific policy decisions within and across subpopulations (i.e., Medicaid, Medicare, privately insured, uninsured individuals, and state prison inmates).
What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver that results from the hepatitis C virus. Acute hepatitis C refers to the first-few-month period after someone is infected. Acute infection can range in severity from a very mild illness with few or no symptoms to a serious condition requiring hospitalization. For reasons that are not known, about 20% of people are able to clear--or get rid of--the virus in the first 6 months without any treatment. Unfortunately, most people who get infected are not able to clear the virus and develop a chronic infection. Over time, chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems, including liver disease, liver failure, and even liver cancer.
How can we respond to Hepatitis C?
With proper and timely treatment, people can be cured of hepatitis C and go on to live healthy, productive lives. The first step for public health officials combating hepatitis C is to choose a screening strategy that maximizes the number of individuals who are aware of their infection. Once diagnosed, people can be treated with antiviral drugs that have high cure rates and minimal side effects. The Hep C State Policy Simulator allows for projecting health and economic impacts for different screening and treatment scenarios. This will help state public health planners to make informed decisions and have the greatest possible impact on hepatitis C in their state with available financial resources.
Visit the CDC website for professional and patient information.
Contact
Jagpreet Chhatwal, PhD
MGH Inst. for Tech. Assessment
Harvard Medical School
101 Merrimac St. STE 1010
Boston, MA 02114 United States
jagchhatwal@mgh.harvard.edu
Acknowledgment
Funding source: The creation of Hep C State Policy Simulator was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention through a Cooperative Agreement Number NU38OT000141 awarded to ChangeLab Solutions; and the National Science Foundation Award numbers 1722614, 1722665, and 1722906. Website's contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Department of Health and Human Services, or the National Science Foundation.